The MSc in Information Studies (IS) programme blends theory and practice to meet the growing demand for skilled information professionals. It equips students with expertise across the breadth of the field, from library science to information analytics, preparing them to lead and innovate in the digital and AI-driven economy.
Graduates will develop both leadership and analytical skills to:
Identify organisational information needs and gaps
Capture, search, organise, classify, analyse, and use information effectively
Build and manage information organisations and systems
Courses cover the full information life cycle—creation, appraisal, capture, organisation, retrieval, analysis, use, preservation, and management of information resources. Emerging topics, such as misinformation and disinformation, are also addressed to ensure graduates are prepared for contemporary challenges in the field.
Learning is highly applied: students build digital libraries using open-source tools, extract actionable insights from social media data, analyse information user behaviour, and design inclusive information products and services. This strong integration of theory and practice ensures graduates are ready to pursue impactful careers in libraries, information-intensive industries, and the growing field of information analytics.


Book a 1-on-1 consultation with our Graduate Team, starting in November, to receive personalised advice, insights on the admissions process, and answers to all your queries!
Don’t miss this opportunity – reserve your spot now by clicking here
- A Bachelor’s degree in an information-related discipline OR
- A Bachelor's degree in any discipline plus full-time work experience in an information-related field.
- Degree classification of second class lower/Honours (Merit) and above or equivalent
- Final-year undergraduates may apply with a provisional degree certificate and/or examination results to date.
- Good communication skills (written and spoken English)
*: Internships are not counted towards full-time working experience.
For undergraduate degree not awarded by an English-medium University or is awarded by an English-medium University but the language of instruction was not English, you must meet the English Language Proficiency Requirement (ELPR).
Minimum Score Required | |
Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) iBT | International English Language Testing System (IELTS), Academic |
|
|
Note: The IELTS sub-scores should not be less than 6.0. The validity period for IELTS/TOEFL scores is two (2) years at the point of application. Please note that only TOEFL or IELTS test scores will be accepted. Also, we do not require the submission of GRE or GMAT test scores.
There is only one intake in August. Applications for August admission will be open in November and close in end January. The outcome of application will be released from end May-June onwards via online.
Programme | Admission Intake | Closing date for submission of online applications with supporting documents |
M.Sc.(Information Studies) [Programme Code: 108] | August | Application Period: 4 November to 31 January |
Applications are to be submitted electronically via the NTU admissions website. Applicants are required to pay a non-refundable application fee of S$50.00 when you send in your admission application per programme applied. Applications without application fee will not be processed.
Applicants may check their application or result status online after receiving the acknowledgement receipt of your application via email.
For more information on the admissions procedures, online application, list of supporting documents application or result status and other relevant details, please click here to view the NTU admissions website.
The programme commences each year in early August and is available in both full-time and part-time. Students are required to complete 30 Academic Units (AU) within their candidature period to be awarded the degree.
Students have two study options:
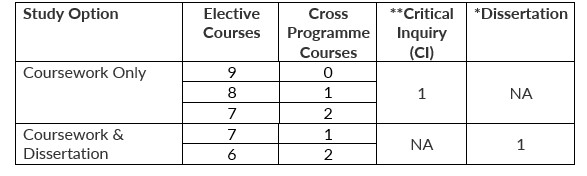
Each course, including Critical Inquiry, carries 3 Academic Units (AUs) while the Dissertation carries 6 AUs.
* To pursue the Dissertation option, students must have a cumulative grade point average (CGPA) of 4.00 or above. Students may require additional semesters to complete their project.
** Critical Inquiry is a group project consisting of three students.
For more information on the Dissertation, please click here.
For more information on Critical Inquiry, please click here.
Candidature
Candidates may apply either for full-time or part-time programme. To be awarded the degree, students will need to complete their programme requirement within their candidature period. A minimum Cumulative Grade Point Average of 2.50 is required to successfully complete the programme.
| Full-Time Candidature | Part-Time Candidature | ||
| Minimum | Maximum | Minimum | Maximum |
| 2 semesters | 4 semesters | 4 semesters | 8 semesters |
| (Note: 1 academic year is equivalent to 2 semesters.) | |||
For more information on Grade Point Average (GPA), please click here.
Old course codes before Semester 1 AY2022-2023

Note: The figure is for illustrative purposes. IS courses may cover more than one aspect of the information life cycle.
IS6702 Research Methods in Human Information Behaviour
This course provides an introduction to research methods as applied in the field of human information behaviour. Students will gain a foundational understanding of the major paradigms and theories of information behaviour, as well as
the principles and techniques of designing and evaluating research studies.
Paradigms in social science and human information behaviour research. Theories and models in human information behaviour. Research ethics. Research
design and procedures. Conceptualization and operationalization. Sampling. Survey research. Experiments. Qualitative research. Nonreactive research. Data analysis methods. Scholarly writing. Evaluation of research quality.
IS6713 Information Representation and Retrieval
This course provides an introduction on how information in different forms of documents can be represented, organised and indexed to support effective search and retrieval. It covers the main concepts of information
retrieval, Boolean and Non Boolean models, use of standards and controlled vocabulary, and the design and evaluation of such retrieval systems.
Description and representation of information sources. Information
retrieval systems principles. Organising information sources. Metadata. Natural language and controlled vocabularies. Information standards. Query structures and matching process: Boolean and Vector Space models. Visualising information.
Designing and evaluating information retrieval systems. Image, multimedia and web information retrieval. Trends in information representation and retrieval.
IS6714 Information Organisation
This course introduces the principles and practices of metadata creation, and the organisation of physical and digital information resources. Students will be given an overview of the prominent standards and tools in resources description, vocabulary
control, classification, and metadata encoding.
Functions and purposes of information organisation systems. Process of metadata creation. Resource description and cataloguing. Descriptive metadata schemas. Authority
control. Subject analysis and access. Controlled vocabulary. Taxonomy and folksonomy. Classification systems. Metadata encoding.
IS6715 Information Management
This course introduces the basic concepts of information management – how information is identified, evaluated, collected, processed, stored and disseminated in profit and non-profit organisations. The emphasis is on context-based
information and its management for planning and decision-making.
Importance of information in society. Information management in learning organisations. Information needs and information seeking in organisations. Information
management at institutional and personal levels. Information management cycle and activities. Managing human, print and online information resources. Organisational information politics models. Information sharing tools and barriers. Role
of information in strategic planning. Information collection through competitor intelligence, business intelligence, social intelligence and the use of ‘big data’ sources. Marketing of information products and services.
Outsourcing of information management activities. Organisational information audit.
IS6717 Information Professions: Heritage, Values and Ethics
This course provides an overview of the broad heritage of information work, to give students an understanding and appreciation of the values/norms that inform this work, as well as the deep roots of many of the problems that continue to confront
the information professions today.
Representing and recording information: from papyrus to ebooks. The social construction of scientific information systems. The tangled history of computing technology. Universal
bibliography: Konrad Gesner to Paul Otlet to Google. Sorting things out: Linnaeus and Buffon to Dewey and Ranganathan. The social role & development of libraries: public, academic and special. Library history in Singapore.
Ethical issues in information work: theories and practical concerns. Contemporary issues in information work.
IS6718 Management of Information Technologies in Organisations
This course examines methods of strategic planning and management of information resources and technologies in libraries and other business organizations. It will cover the latest trends of the continuing evolution of library-related applications and other organizational information technologies. The challenges and opportunities presented by such rise of advanced technologies will also be explored. Tools and techniques for planning, implementing and managing technological change for libraries and information services in organisations. Technologies in organisations computing basics, network and database applications, libraries systems, collaborative software, communication technologies, social software, mobile software services and big data technologies. Human computer interaction and social aspects of information technologies.
IS6721 Collection Development and Management
This course covers the principles and techniques used for developing, managing, and evaluating print and non-print materials. Students will also learn about the impact of contemporary issues including intellectual freedom, copyright and censorship
on collection development and management activities.
Key concepts related to collection development and management. Community analysis and information needs assessment. Formulation of resource development and management
policy. Censorship and intellectual freedom. Selection approaches and tools. Role and evaluation of library vendors. Access to and management of electronic information resources. Patron-Driven Acquisitions. Library consortia for collaborative
collection development. Licensing and contract negotiation, Financial planning for collection development. Conservation and preservation of materials. Evaluation of collection using a variety of collection-centred and user-centred techniques.
De-selection of materials.
IS6722 Cataloguing and Classification
This course covers cataloguing and classification principles and practices, with special emphasis on the standards and systems in the library communities. Students will gain experience in conducting cataloguing work, which include bibliographic
description, authority control, subject cataloguing, classification, and MARC encoding. A concentrated focus will be on the description and access of digital resources.
Principles and processes of bibliographic control.
Bibliographic description standards (AACR2r, RDA). Name-title authority control. Subject cataloguing and indexing. Bibliographic classification (LCC). Faceted classification. Encoding of bibliographic records (MARC21). Descriptive and subject
cataloguing of digital materials. Bibliographic utilities and integrated library systems (OCLC Connexion).
Prerequisite: Information Organisation or Instructor’s consent.
IS6723 Business & Management Information Sources & Services
This course provides an overview of the wide world of business information sources and services. Students will be exposed to the dimensions of business information, and both print and electronic resources. The types of business information services
that can be provided by libraries and information centres will also be looked at.
Business print resources and databases. Government sources and services for business. Economic and industrial indicators. Marketing information
resources. Investment information resources. Corporate information needs and services. Competitive intelligence and business. Intellectual property issues. Future trends in the provision of information to business.
IS6724 Children & Young Adults Information Sources & Services
This course provides basic knowledge of children/young adult literature, the value of that literature in child development, and an understanding of the information needs of children and young adults in the digital age.
History
of children’s literature. The importance of children’s literature. Preschool and primary years. Young adult literature. Electronic information sources for children & young adults. Information services. Storytelling and read alouds.
Folktales & mythology. Special collections.
IS6729 Organisational Records Management
This course introduces the main concepts and practices of managing records in organisations. It equips students with the necessary knowledge and skills to prepare them as managers of records in organisations.
Foundations
and importance of records management. Analysing the context of records. Record creation and capture. Managing the appraisal, retention and disposal of records. Records storage and preservation. Design and implementation of records
management. Disaster planning and recovery.
IS6730 Digital Libraries
This course aims to introduce you to the foundation and development of digital libraries. The rapid growth in born-digital content and digitized resources has increased the demand for many institutions (including libraries, memory institutions, governments, and commercial enterprises) to build digital collections. The course aims to equip you with the theoretical knowledge and technical skills to build digital libraries using open-source tools. You will learn how information methods and techniques—such as metadata, taxonomy, XML, full-text indexes, Web applications, and database systems—are used together to build digital libraries. This course has an emphasis on technical aspects; you will gain hands-on experience building digital libraries using digital library building tools.
IS6734 Reference and Information Discovery
This course develops basic searching skills to effectively retrieve information using different information systems. It also familiarises students to key reference sources and activities, and how to manage a reference service.
Basic searching concepts and developing search strategies. Use of basic and advanced search features of a retrieval system. Various search techniques and result refinement. Use of database thesauri. Selection of online vendors and databases.
Evaluation of search results. History and philosophy of reference service. Evaluation and selection of key reference sources. Conducting reference interviews. Marketing and promotion of information services. User education and instruction.
Evaluation of reference services. Virtual reference services. Changing role of information professionals in new reference environment.
IS6750 Social Media Analytics
This course develops analytical ability with respect to the variety of information provided by the web and social media applications. In providing an overview of cutting-edge social media analytics with an emphasis on applications to real life
problems, students will learn about the mechanisms for observing behavioural and consumer generated information as well as the leading-edge technologies that aid in the collection and analysis of these data.
Techniques
for managing, exploring, visualizing, and analysing data from social media applications. Strategic aspects of social media analytics. Metrices for assessing the effectiveness of social media strategies. Collecting, analysing and
deriving insights from social media data. Social Network Analysis.
IS6751 Text and Web Mining
This course is an introduction to text and web data mining. Students will learn how to analyse unstructured data (i.e. text contents), hyperlinks, and usage data on the Web using text and data mining techniques. The basic concepts of data mining: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and semi-supervised learning. Text mining: natural language processing and information extraction. Web mining: web crawling, web usage mining, and semantic web. Opinion mining and sentiment analysis. Tools for web data mining.
IS6752 Data Extraction Techniques
This course covers how to obtain data from the web, and prepare retrieved data in various formats for further analysis. Students will learn various data crawling techniques and tools both through lectures and hands-on exercises in labs. Principles and concepts of data collection and preparation; Data gathering techniques: Web crawling, APIs for Social media data collection; Database definition and manipulation: structured query language, transaction processing, and access control; Client-side technologies: Web content representation with mark-up languages and dynamic Web page generation with script languages. Server-side technologies: application programming languages.
IS6753 User Metrics and Analytics
This course examines metrics and analytics of users’ online and offline preferences and behaviours. It introduces principles, techniques, and new technologies for measuring and analysing users’ experiences with information services, online platforms, and information technologies. Students will learn to capture, visualise, analyse, and evaluate a variety of user metrics, including cognitive, affective, behavioural, physiological, performance-related, and geospatial measures.
IS6754 Disinformation and the Information Professions
3. Develop an ability to constructively critique potential responses to the issue of disinformation/misinformation.
IS6755 Inclusion by Design: Disability and Digital Inclusion
Internationally, disability inclusion and the digital has come under the spotlight since the advent of the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. In Singapore and across Asia-Pacific, both state actors, transnational bodies, and also corporates are increasingly focused on disability and digital inclusion. Amidst this global push, what does it mean to do and achieve digital inclusion? What aspects, issues, policies, standards, and practices impinge on digital inclusion? How can we contribute to and create digital inclusive practices and/or policies? Across the course, we will spotlight current cases/examples/practices with a specific focus on Asian contexts.
IS6791 Social Sciences & Humanities Sources & Services
This course seeks to broaden students understanding of electronic and print information sources, focusing specifically on the areas of social science and the humanities. It seeks also to contextualize the use of these tools within the wider world of specific social and humanities domains of knowledge production.
At the end of this course students will; 1) Have an understanding of the social worlds of three social science or humanities disciplines. 2) Be aware of the major information tools for the social sciences and humanities. 3) Have an understanding of the role of government in the production of information in the social science and humanities.
Research Project
IS6799 Critical Inquiry
Role of critical thinking, evaluation and research in information and knowledge work; steps in carrying out a research project: problem identification, critique and review of research; selection and use of theoretical framework, methodological design, data collection and analysis; developing a research proposal; communicating research results; assessment and use of results of research studies; ethical concerns and issues associated with research.
Cross-listed Courses from Other Programmes
IN6204 Software Project Management
This course is an introduction to software project management concepts and management. Core issues that will be looked at include Project communication and documentation; Risk Management; and Best Practices. Students will examine case studies in project management to better grasp the various areas of software project management.
IN6207 Human-Computer Interaction - Users, Tasks & Designs
In this course students will be given an introduction to general design and usability issues, with respect to key cognitive and physical human capabilities and their relations to the design of usable and useful systems. The course will also look at international design heuristics and guidelines from three perspectives: cultural, ethical and legal, and relate design and usability methods to the wider systems development process.
IN6221 Information Visualisation
This course will examine the study of concepts, models and examples for improved information visualisation. Students will look at representation and interpretation data, as well as different forms of document visualisation such as TileBars, galaxies, themescapes, and Kohonen maps.
IN6229 Management of Information Systems Outsourcing
This course provides an overview of management of IS outsourcing, which includes planning and management of IS outsourcing, sourcing strategies, models, related legal issues, and managing global IS outsourcing. Students will also examine risk mitigation practices and best practices and case studies of IS outsourcing.
KM6308 Business Intelligence
Business intelligence in the corporate environment: application, systems and processes. Characteristics of competitor, competitive and social intelligence. Business intelligence and growth opportunities: political, economic and social environments. Business intelligence strategies and systems. Business intelligence in various contexts: product, customer and supplier. Internet and Web-based intelligence. Ethical issues related to business intelligence.
KM6312 Information Mining & Analysis
Principles and concepts of knowledge discovery and data mining. The knowledge discovery process. Data preparation. Techniques and methods for extracting information and knowledge from large amounts of data. Statistical methods. Machine learning techniques: decision tree induction, nearest neighbour categorisation, Bayesian learning, neural networks, association rules, and clustering. Text and Web mining for unstructured data. Data mining for KM applications.
Academic Integrity
- The use of words, images, diagrams, graphs, or ideas derived from books, journals, magazines, visual media, and the internet without proper acknowledgement;
- Copying of work from the internet or any other sources and presenting as one’s own; and
- Submitting identical work for different courses or to different journals and publications.
- Online/softcopy assignments: Students are required to attach their assignments with a softcopy of the signed declaration of authorship form as one document for online submission.
- Hardcopy assignments: Students are required to attach the hardcopy declaration of authorship form on the front page of their written assignments for hardcopy submission.
Please check with respective course instructors if your written assignment requires the declaration forms.
Course Fees
The substantial tuition subsidy from the Government of Singapore comes in the form of a MOE subsidy which is administered by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and is offered to eligible students up to the normal course duration (one year for full-time
students and two years for part-time students). Students who take longer than the normal course duration will be liable for non-subsidised (Full) tuition fees during the extended semesters. Students need not apply for the MOE subsidy if they are eligible.
Note: From AY 2019 onwards, MOE subsidy only applies to Singaporean and Singapore Permanent Resident (SPR) students. International students applying for Coursework Programmes will be liable for non-subsidised tuition
fees.
Fee for Academic Year 2025-2026
| Description | Fees (in S$) | Remarks |
| Application Fee | 50.00 | Non-refundable and payable during application. |
| Deposit Fee | 2,500.00 | Non-refundable and non-transferable (This is required upon the acceptance of the offer and will be used to offset your tuition fee payment.) |
Tuition Fees for Academic Year 2025-2026
| Tuition Fees per Academic Year (AY2025-2026) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSc in Information Studies (IS) Programme Status | Non-Subsidised Fees | Singapore Citizen | Singapore Permanent Resident | |
| S$ | S$ | S$ | S$ | |
| Full-time | 42,320 | 9,800 | 18,050 | |
| Part-time | 21,160 | 4,900 | 9,025 | |
Notes on tuition fees
• All fees stated are Singapore Dollars and are inclusive of GST charges.
• The programme fees are reviewed annually and may be revised. The University reserves the right to adjust the programme fees without prior notice.
Tuition Fees for Academic Year 2024-2025
| Tuition Fees per Academic Year (AY2024-2025) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSc in Information Studies (IS) Programme Status | Non-Subsidised Fees | Singapore Citizen | Singapore Permanent Resident | |
| S$ | S$ | S$ | S$ | |
| Full-time | 41,900 | 9,750 | 17,400 | |
| Part-time | 20,950 | 4,875 | 8,700 | |
Notes on tuition fees
• All fees stated are Singapore Dollars and are inclusive of GST charges.
• The programme fees are reviewed annually and may be revised. The University reserves the right to adjust the programme fees without prior notice.
Tuition Fees for Academic Year 2023-2024
| Tuition Fees per Academic Year (AY2023-2024) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSc in Information Studies (IS) Programme Status | Non-Subsidised Fees (inclusive of GST) | Singapore Citizen | Singapore Permanent Resident | |
| S$ | S$ | S$ | S$ | S$ |
| Sem 1 | Sem 2 | |||
| Full-time | 20,350 | 20,540 | 9,750 | 16,750 |
| Part-time | 10,175 | 10,270 | 4,875 | 8,375 |
Notes on tuition fees
• All fees stated are Singapore Dollars and are inclusive of GST charges.
• The programme fees are reviewed annually and may be revised. The University reserves the right to adjust the programme fees without prior notice.
Graduation Requirements
Course Load and the Academic Unit System
With the introduction of the Academic Units system in the university, the Master by Coursework programme students have to accumulate a total of 30 Academic
Units (AUs) to graduate. Each course in the curriculum carries 3 AUs, with the exception of the Dissertation Project which carries 6 AUs. A 3-AU course comprises 39 contact hours of lectures, tutorials and laboratory
work (unless otherwise specified).
Grade Point Average Requirements
The university adopts a Grade Point Average (GPA) system of calculating the overall academic performance of a student in a particular semester and for the whole programme. Letter
grades obtained for courses are assigned grade points of 0 to 5.0.
For more information on GPA, please refer to this link.
The Term Grade Point Average (TGPA) represents the grade point average for all courses taken by a student in a particular semester. The Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) represents the grade point average for all the courses
taken by the student.
Poor Academic Performance
A coursework student with poor academic performance will be subjected to the following actions:
- Academic warning if TGPA < 2.50 in any term of study
- 2. Termination of Candidature if TGPA < 2.50 for the second consecutive term of study.
A student is considered to be making satisfactory progress in any semester of study if he or she attains a minimum TGPA of 2.50. A student who obtains a TGPA of less than 2.50 in 2 consecutive semesters of study will be dismissed from the programme.
To meet the academic requirement for graduation, a student must:
- Complete all the requirements for the programme of study, and
- Attain a minimum CGPA of 2.50 at the completion of the programme of study.
FAQs
Refer to a list of Frequently Asked Questions here

