Polymers for Additive Manufacturing
Web of Science's Hot Paper by Assoc Prof Zhou Kun

Additive manufacturing (AM) is considered essential to Industry 4.0 due to the unparalleled design freedom that it offers, reduced material wastage, and the low-volume production of customisable products on demand. In particular, polymers and their composites are widely employed in AM owing to their intrinsic low density and corrosion-resistant properties and the potentially excellent mechanical, thermal, electrical, and biocompatible properties of the printed parts.
The article provides a comprehensive assessment of the recent progress in the development of polymer materials for different AM techniques (Fig. 1). With extensive experience in powder bed fusion research, Assoc Prof Zhou and his team present the principles of AM techniques, requirements for material printability, and insights into the major challenges and potential research directions of the technology, aiming to inspire its further development. Additionally, an overview of guidelines for material development is given, and notable advances in polymer AM techniques implemented in the aerospace, automotive, electronic, and medical industries are discussed.
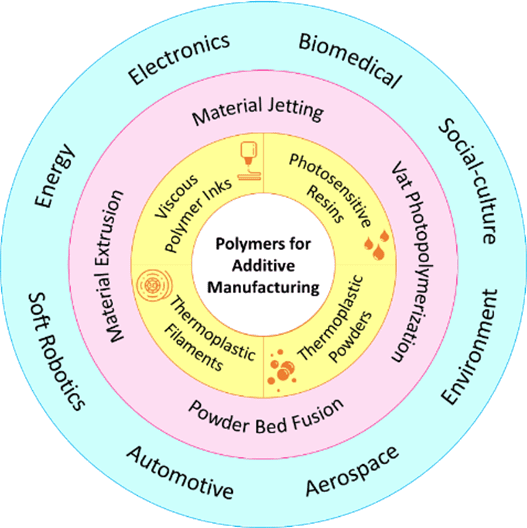
Fig. 1. Overview of polymer materials employed in typical polymer AM techniques and their applications.
Assoc Prof Zhou leads a research group comprising experts in mechanics of materials and AM. He has spearheaded several industrial projects involving the development of polymer composites with enhanced mechanical properties in collaboration with reputable international corporations such as HP Inc., Bosch, and PTT Global Chemical. His combination of experimental and computational research has resulted in the advent of novel materials with huge market potential, for which two US patents have been filed.
References
Lisa Jiaying Tan, Wei Zhu and Kun Zhou, “Recent Progress on Polymer Materials for Additive Manufacturing”, Advanced Functional Materials 2020, 30(43), 2003062, DOI 10.1002/adfm.202003062.
Web of Science’s Hot Paper | 119 Citations (as of 2 March 2022)







