Foveal Machine Vision Method and System for Enhanced Capsule Endoscopic Imaging
Synopsis
This invention applies foveal machine vision to capsule endoscopy, combining attention-driven imaging, adaptive radios, and visual–inertial fusion to improve gastrointestinal (GI) diagnostics. It enhances detection accuracy, reduces repeat procedures, integrates seamlessly with clinical workflows, and remains outpatient and sedation-free for patients.
Opportunity
The foveal machine vision method is a well-established human-eye-inspired technology that mimics the way our eyes focus on details in the centre of vision (the fovea) while keeping peripheral areas in lower resolution. The current invention applies this mature principle to capsule endoscopy. By integrating attention-driven imaging, adaptive radios, and visual–inertial fusion, it delivers a uniquely efficient and clinically relevant solution for fewer missed diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
For clinicians, the system integrates seamlessly with existing PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System) and EMR (Electronic Medical Record), requires minimal onboarding, and mirrors current reading habits. It streamlines the review process while ensuring clinicians retain full control by accepting or editing findings before making the final decision.
For patients, the examination remains outpatient and sedation-free, with no disruption to daily activity, while improved targeting and localisation help reduce the need for repeat procedures.
This technology overcomes key limitations of current capsule endoscopy in gastrointestinal (GI) diagnostics — namely low image resolution (~500 X 500 pixels), slow frame rates (<5 frames per second), and excessive energy use — that can compromise lesion detection and often necessitate repeat procedures.
Ideal collaborators include R&D partners to advance development, gastroenterology departments for clinical validation, device manufacturers for capsule integration and scaling, and telemedicine providers to enable remote diagnostic deployment.
Technology
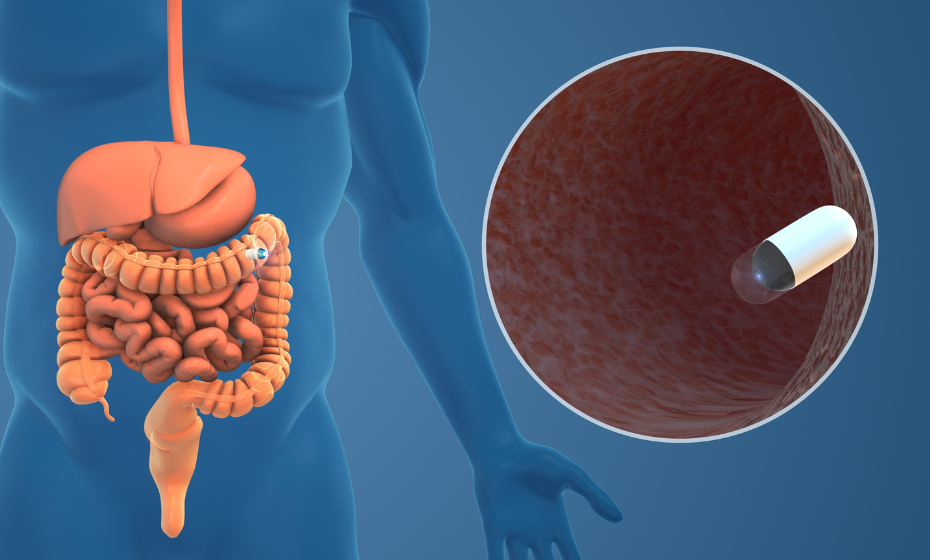
The system is a swallowable capsule endoscope with a high-resolution imaging sensor, real-time AI inference engine, and wireless transmission module. It operates in a continuous loop in two modes mimicking human visual attention:
- A routine low-power full-field scanning mode
- An intelligent focus mode: high-resolution, high-frame-rate, which is activated upon the detection of suspected abnormalities. The adaptive radio then transmits the additional data efficiently, while the server integrates video and inertial cues to estimate position, performs multi-class diagnosis, and generates a structured report with linked evidence.
The technology has already achieved successful laboratory validation of its key modules, including fast-switching imaging from full field to region of interest, robust wireless link and power control in benchtop and tank models, offline lesion detection on curated datasets, and visual–inertial localization on recorded trajectories.
The next step is to bring these proven capabilities together into a unified capsule form factor, advancing through ex vivo and simulated validation toward clinical translation. With a strategy that prioritizes high sensitivity for clinically relevant lesion classes, while ensuring acceptable precision and clear evidence trails, the platform is well-positioned to progress rapidly toward higher TRLs in collaboration with clinical partners.
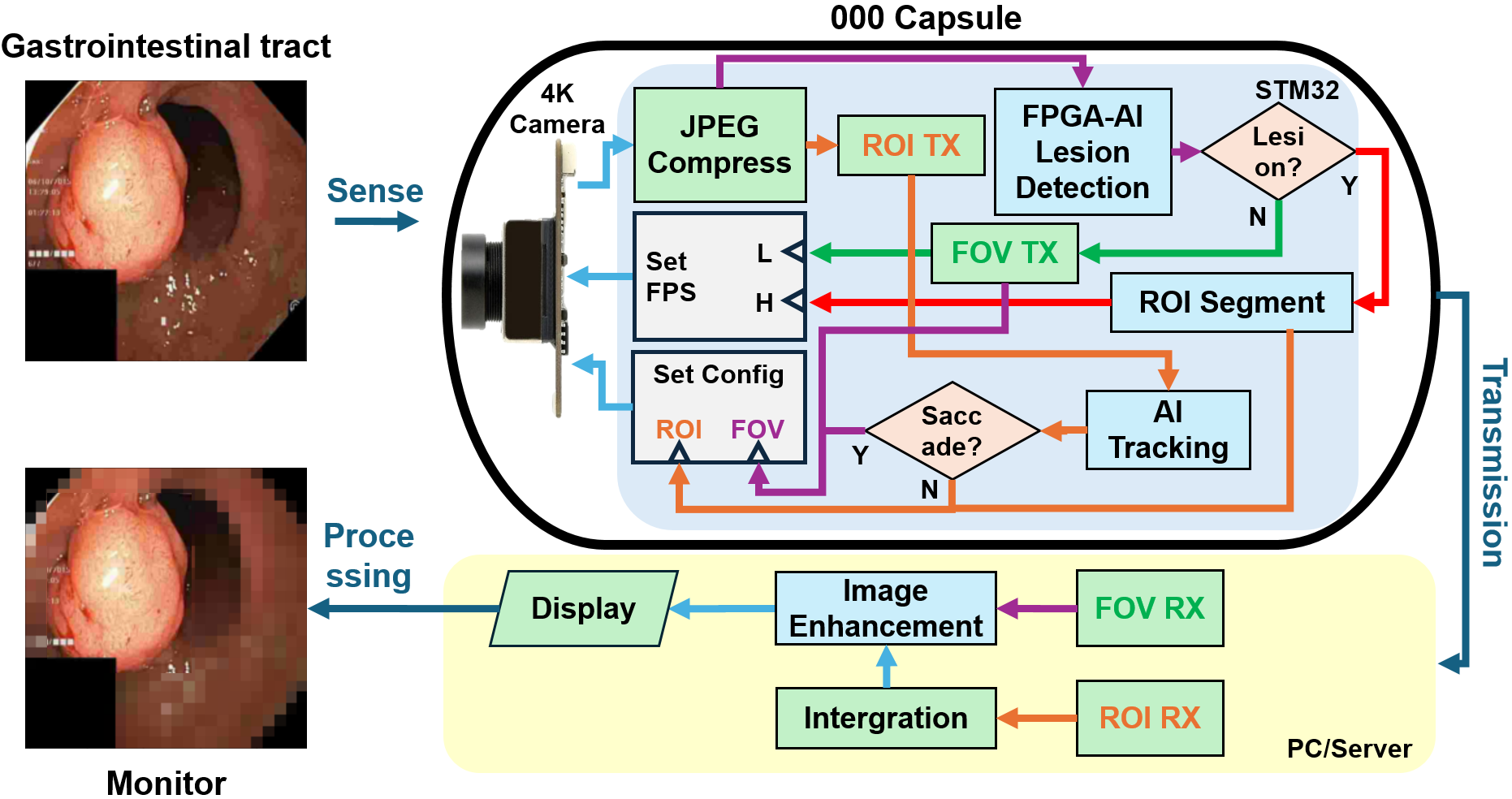
Figure 1: Foveal Machine Vision Method Algorithm
Figure 2: Dual-mode capsule endoscopy balances low-power scanning with high-resolution lesion tracking, delivering clearer images while conserving energy
Applications & Advantages
This technology can be deployed in the healthcare diagnostics industry, particularly for gastrointestinal (GI) disease screening and monitoring. It is suitable for hospitals, endoscopy centres, and telemedicine services that require non-invasive and accurate diagnostic tools. Foreseeable applications include the early detection of obscure GI bleeding, polyps, and cancers.

-and-dr-dorrain-low-from-ntu-singapore's-lkcmedicine.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=b389b500_1)
.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=82921582_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=ba129532_1)