Infrastructure-Free Smartphone Indoor Localization Using Room Acoustic Responses
- Indoor smartphone location recall by recognizing acoustic echo patterns
Smartphone-based localization has attracted wide research in recent years due to the proliferation of smartphones and the increasingly demanded location-aware services. In indoor environments, the global positioning system (GPS) are often unavailable due to the blockage of GPS signal and more stringent requirements of indoor positioning services. Therefore, a number of modalities such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are exploited to build smartphone-based indoor localization systems. These solutions are usually infrastructure-based, which require the installation of extra anchor points for localizing the smartphones. Excessive effort for infrastructure installation often stems the applicability of infrastructure-based indoor localization systems. Therefore, an accurate, reliable infrastructure-free indoor localization system will be more favorable compared with infrastructure-based systems.
EchoLoc is a deep neural network (DNN) based system for accurate and large-scale smartphone indoor localization using room acoustic responses. It has four salient advantages.
- EchoLoc is infrastructure free and only requires the access to the smartphone audio system. We show that the potential applications of EchoLoc span from small meeting rooms to large semi-open concert halls.
- EchoLoc achieves 95% location recall accuracy in a large public indoor space and sub-meter mean localization error in the tested lab office. This localization accuracy can support a range of location-based mobile services such as navigation, way finding, workspace clock-in, artwork interaction, emergency response, etc.
- EchoLoc works with normal hand grasping of the smartphone and require no special holdings of the phone.
- EchoLoc emits chirps in a frequency range from 15 kHz to 20 kHz, which lies in the nearly inaudible range of human ears. Therefore, EchoLoc is robust to ambient noise and causes little/no annoyance to users.
There are a few recent works exploiting smartphone acoustic system for indoor localization. However, they only achieve room-level localization or only evaluate the localization performance at a few locations per room.
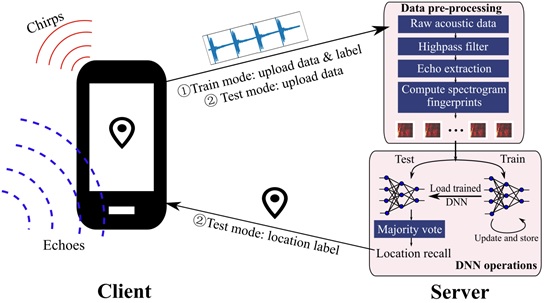
Fig. 1 Workflow of EchoLoc
EchoLoc performance is evaluated in a public indoor space and a lab area. Among the 101 fingerprinted locations in a large scale public indoor space, EchoLoc achieves a 95% location recognition accuracy (Fig. 2). Among the 61 locations fingerprinted in our lab area, EchoLoc achieves an 81% location recognition accuracy and sub-meter mean localization error (Fig. 3).

Fig.2 Confusion matrix in public indoor space (101 positions, 95% accuracy)

Fig.3 Localization error in lab area (61 positions, 81% accuracy)
EchoLoc can support a range of location-based mobile services such as navigation, way finding, workspace clock-in, artwork interaction, emergency response, etc., in various indoor environments.
To give some example, in an office building, EchoLoc can be used for employee clock-in or phone-nearby required device unlock. In a large shopping mall, EchoLoc can help customers to locate their positions and provide guidance toward a specific shop. In a hospital, EchoLoc can be used for patients’ location monitoring and emergency response. In a gallery or museum, visitors can trigger the narration of an artwork using EchoLoc just in front of it.
Dongfang Guo, Wenjie Luo, Chaojie Gu, Yuting Wu, Qun Song, Zhenyu Yan, Rui Tan. 2021. "Demo Abstract: Infrastructure-Free Smartphone Indoor Localization Using Room Acoustic Responses." In The 19th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems (SenSys ’21), November 15–17, 2021, Coimbra, Portugal. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 2 pages.
