Knowledge-Enhanced Conversational Recommendation via Transformer-based Sequential Modelling
Synopsis
A new model for conversational recommendation system (CRS), which can be potentially used in applications such as ChatBot.
Opportunity
In general, a recommender system learns user preference from historical user-item interactions, and then recommends items of user's preference. The recommended items can be delivered to users through various interfaces depending on the task, e.g., a list of recommended products on e-commerce websites. Thanks to the rapid development of chatbots, Conversational Recommender Systems (CRS) is now becoming a promising interface to deliver recommended items to users directly through dialogues. Our techniques improve the accuracy of CRS systems.
Technology
We propose a transformer-based sequential conversational recommendation method, named TSCR, to model the sequential dependencies in the conversations. In TSCR, we represent conversations by items and the item-related entities, and construct user sequences to discover user preferences by considering both the mentioned items and item-related entities. Based on the constructed sequences, we deploy a cloze task to predict the recommended items along a sequence. We further extend TSCR by leveraging knowledge graphs in the following ways: (a) we utilise knowledge graphs to train representations of items and item-related entities offline and use them as initialised representations in the model; and (b) given the rich structural information of knowledge graphs, we augment the user sequence of conversations with the multi-hop paths between two nodes (i.e., items or item-related entities) in knowledge graphs and then train the model based on the augmented sequences. An illustration of the technology is shown in Figure 1.
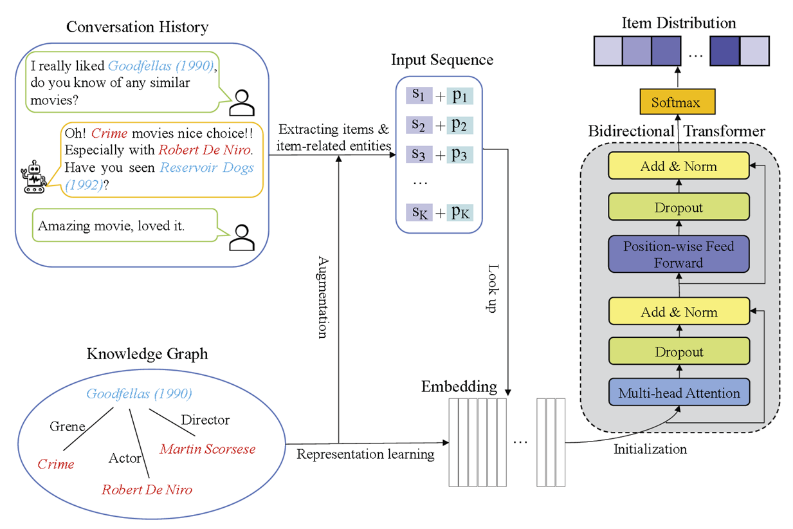
Figure 1: The overview of TSCR method - a transformer-based sequential conversational recommendation method to model the sequential dependencies in the conversations, which is further extended by leveraging a knowledge graph for representation initialisation and sequence augmentation.
Applications & Advantages
- Existing solutions do not model the potential sequential dependency within the conversations. Our TSCR model can greatly improve the performance of CRSs by capturing the sequential dependency.
- TSCR captures the spatio-temporal relationships of items and item-related entities by combining the modelling of sequential dependency (temporal relationships) and knowledge graphs (spatio relationships).
Some case study results are shown in Figure 2.
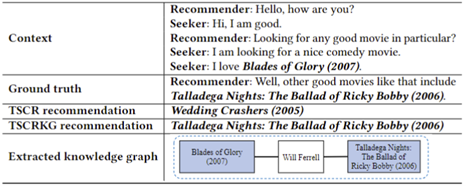
Figure 2: A case study result on the ReDial dataset.
In this case, TSCRKG was able to acquire a knowledge graph by connecting the movies “Blades of Glory (2007)” and “Talladega Nights: The Ballad of Ricky Bobby (2006)” through a common factor, which is the actor “Will Ferrell” who appeared in both movies. This complete path in the knowledge graph allows improved explainability for the recommended results. Additionally, it confirms the effectiveness of TSCRKG and the benefit of incorporating the knowledge graph and sequential modelling.



.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=462ec612_1)











