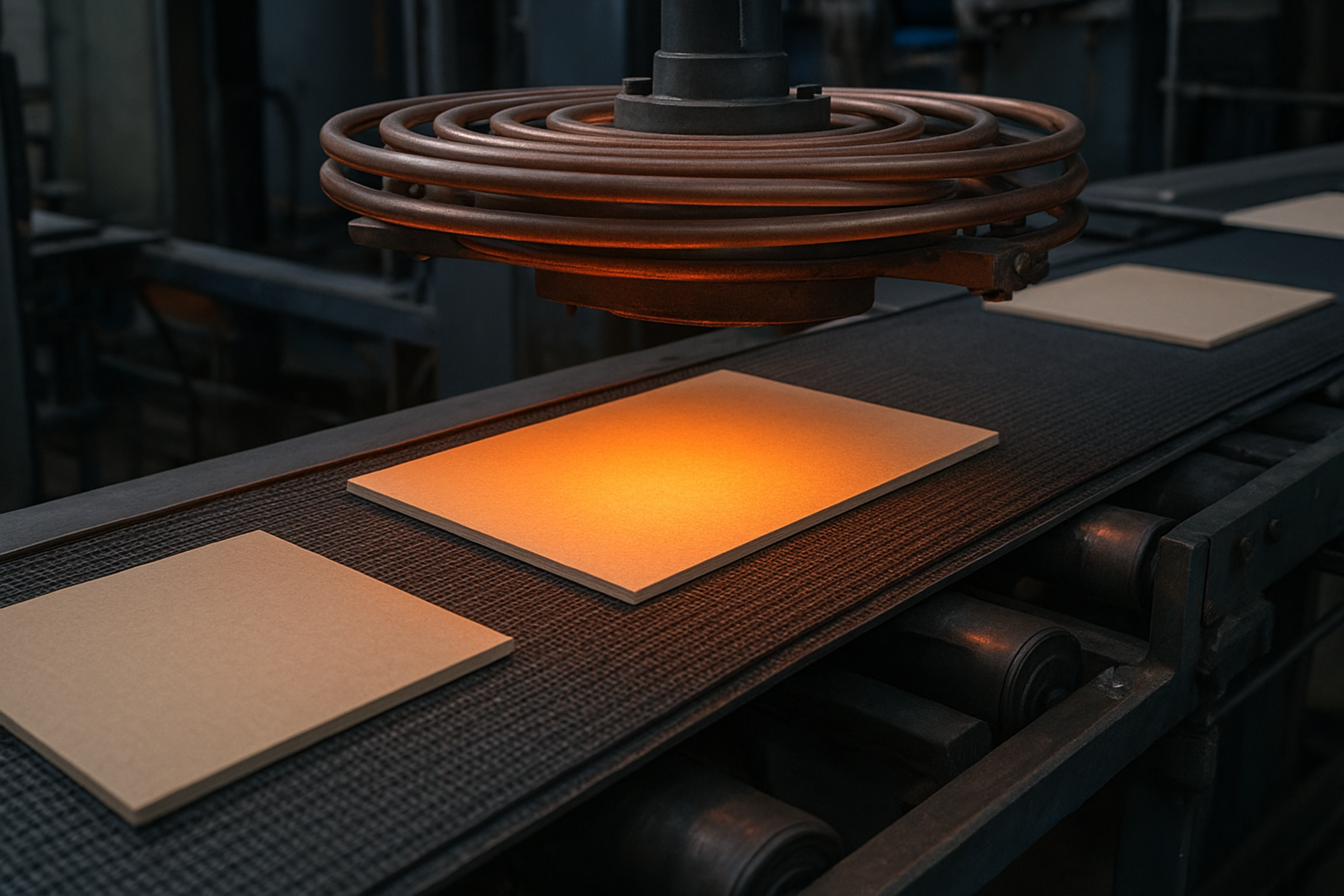
Temperature-Modifying Induction Curing Additives
Synopsis
This technology introduces induction heating into plastics for the first time, enabling automated, energy-efficient manufacturing of thermoset and thermoplastic resins. By using ceramic particle additives to convert magnetic fields into heat, it allows rapid, non-contact curing and bonding, replacing ovens and autoclaves. Applicable across automotive, sports, and green energy sectors, it offers scalability, sustainability, and new design possibilities.
Opportunity
Manufacturing with plastics, particularly thermoset and thermoplastic resins, has long been constrained by inefficient and energy-intensive heating methods. Current practices rely on large ovens, autoclaves, or surface heating techniques using gas or electric conduction. These approaches not only consume significant energy but also require prolonged processing times and manual interventions, limiting scalability and automation.
This technology bridges induction heating into plastics for the first time. This creates opportunities for automated, energy-efficient manufacturing of thermoset (epoxy/urethane) or thermoplastic resins not possible through other surface heating methods. This disruptive manufacturing technology allows volumetric heating of plastic parts required in automotive, sports, and green energy sectors. Non-contact, volumetric heating occurs through incorporation of specially designed ceramic particle additives. The additives convert magnetic fields to heat for activation of adhesives, coatings, or melting of thermoplastics. This technology replaces inefficient fabrication methods such as energy-intensive ovens, autoclaves, and surface gas/electric conduction-based heating. Induction provides remote activation, real-time feedback, and external digital manipulation for a new paradigm of assembly design intents. This innovative transformation removes labour-intensive manufacturing methods and aligns with current goals of energy efficiency and long-term sustainability.
The technology owner is actively seeking R&D collaborations, licensing partnerships, and IP acquisition opportunities with manufacturing companies in adhesives, sporting goods, and automotive manufacturing.
Technology
Induction technology for plastic manufacturing allows instantaneous heating.
Additive technology exploits particles that convert magnetic fields to heat.
Imparts remote, on-demand activation of adhesives through other materials.
Integrates with automated assisted manufacturing, in-line production.
Provides real-time processing feedback, with a 50–300°C temperature range.
Heating gradients of 0.1–2°C per second are achievable.
Technology can be used for both bonding and later debonding.
Applicable to plastics, adhesives, coatings, rubbers.
Additive technology, no reformulation required for proprietary resins.
Ceramic additives, chemically inert, stable to 600°C.
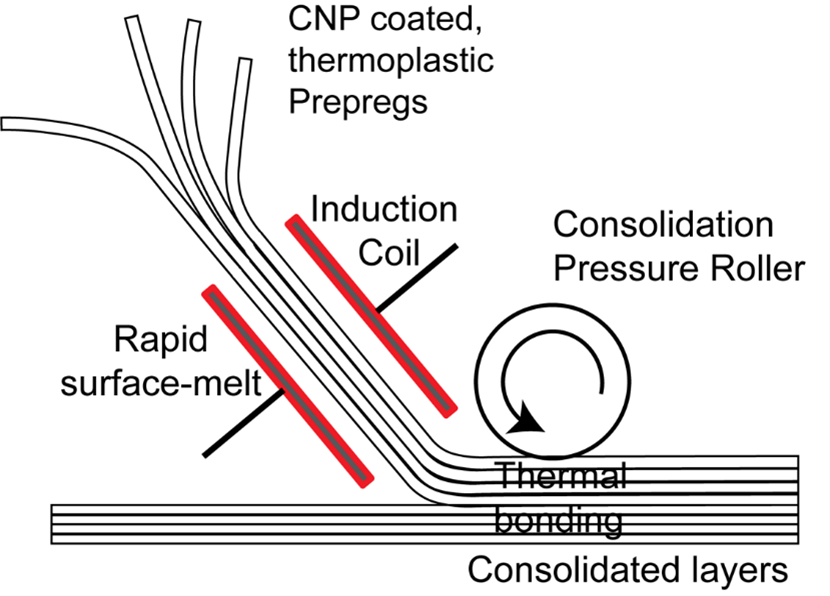
Figure 1: The image shows how induction coils rapidly heat thermoplastic prepregs, which are then pressed by a roller to form consolidated bonded layers.
Applications & Advantages
- Shoes & Foams: Precise activation of adhesive films at specific stations
- Paints & Coatings: Non-contact curing/drying of resins 0.1–5 mm thick
- Composites & Laminates: Instantaneous curing/melting of parts 1–50 mm deep
- Complex Assembly: Bonding of internal substrates after assembly
- New Process: Design and separation of independent fabrication processes



.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=40b426f_1)
.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=29c7e020_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=3b74ec1c_1)