
A Neural Fictitious Self-Play-Based Approach for Solving Large-Scale Escape Interdiction Games
Synopsis
This technology proposed neural fictitious self-play (NFSP), a deep learning-based method, to solve large-scale escape interdiction games. NFSP offers applications in law enforcement, resource allocation and traffic management, and shows significant potential for real-world impact and commercial applications.
Opportunity
The invention provides an approach for solving large-scale escape interdiction games (EIGs), which have wide-ranging applications in solving real-world problems.
- Guiding law enforcement to interdict escaping criminals is the most straightforward application. With millions of urban crimes occurring daily, optimising the deployment of police officers can significantly contribute to reducing crime rates.
- The invention can help government entities or police departments to adjust the number of police resources in an area. For example, we can use the method to calculate the probability of successful interdiction under the worst situation. If the value is below a certain threshold, more police officers should be deployed in the area.
- The invention can be used to stop speeding vehicles. Speeding is a grave concern in many cities. To reduce the number of speeding-related accidents, stopping speeding when it happens is crucial. It can also assist traffic police in adjusting their interdiction strategy.
Technology
This invention proposes a novel learning paradigm which enables NFSP, a deep learning-based method for solving NE (Nash Equilibrium) in large-scale EIGs. Specifically, it voids explicitly learning states-to-actions mappings. Instead, it trains deep neural networks (DNNs) to map state-action pairs to values, which may represent Q-values or probabilities.
The main novelties are four-fold. First, we enable an NFSP agent to approximate best response (BR) policy in EIGs by learning action representations, which are used as a part of BR policy networks inputs.
Second, we address the difficulty of approximating average policy in EIGs by forcing an NFSP agent to only assign distributions over legal actions at each state.
Third, we propose learning efficient graph node embeddings by node2vec to leverage information contained in urban road networks.
Fourth, we reformulate the BR of the attacker as a multi-armed bandit problem to avoid unnecessary exploration on non-escaping routes, and we design two auxiliary modules, namely the AVGer and the Cache, to fit the reformulation into the framework of NFSP.
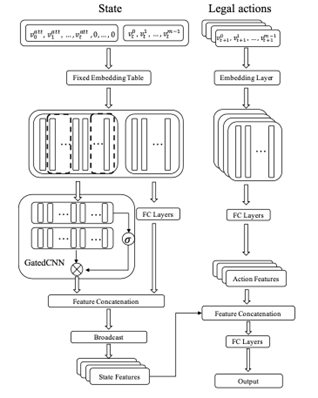
Figure 1: The neuron network architecture of the defender.
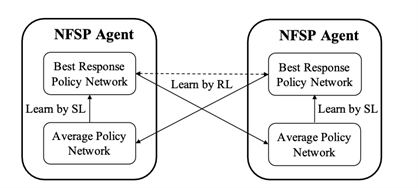
Figure 2: Details of the NFSP framework.
Applications & Advantages
The invention is a sampling-based model-free approach and is equipped with deep neural network approximation. Its main advantages over existing methods are:
- Good scalability and able to model complex environments as long as sufficient samples are collected from the environment.
- Model-free and does not require any delicate domain-specific design. The implementation and deployment are easy and straightforward. It can also be easily adapted for games which hold similar property with EIGs.
- Overcomes the limitation of memory. Existing approaches require the storage or enumeration of all escaping paths, which is not feasible when the state and action space are large. Using deep neural network to approximate policy overcomes this problem, making this approach capable of solving complex real-life problems.



.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=462ec612_1)











