
Portable Electrostatic Evaporative Cooling Enhancer for Food & Pharma Cold Chains
Synopsis
This Portable Electrostatic Cooling Enhancer uses a low-power ionic wind to boost evaporative cooling, providing adjustable sub-ambient temperatures with minimal energy. Compact and efficient, it enables reliable cold storage for food, pharmaceuticals, and vaccines, especially in regions with limited infrastructure.
Opportunity
Reliable cold storage is critical for preserving food and pharmaceutical products, yet conventional refrigeration requires a stable electricity supply that is often unavailable in underdeveloped regions. Traditional passive evaporative cooling methods, while centuries old, are highly dependent on ambient humidity and temperature and lack consistent performance.
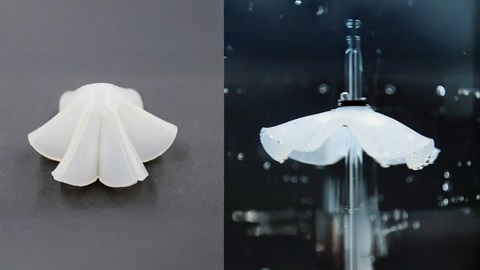
This technology introduces a Portable Electrostatic Cooling Enhancer that enhances evaporative cooling using a low-power electrostatic generator. By generating a gentle ionic wind directed at an evaporating medium such as a hydrogel, the device significantly accelerates evaporation and boosts cooling power with minimal energy input. The cooling strength can be adjusted easily by tuning the electrostatic generator, allowing goods to be maintained at desirable sub-ambient temperatures even under fluctuating environmental conditions.
Compact and energy-efficient, this innovation has the potential to support cold-chain logistics operators, food and grocery delivery platforms, and pharmaceutical distributors, particularly in regions with limited infrastructure. Its portability also makes it suitable for widespread adoption across supply chains, ensuring reliable access to fresh produce, medicines, and vaccines.
Technology
The cooling enhancer consists of microelectrodes arranged with a grounded electrode, powered by a portable, battery-driven electrostatic generator. As the generator is switched on, air molecules in the vicinity of the microelectrodes are ionised and attracted towards the ground electrode. As they travel across the air gap, an ionic wind that blows towards the cooling medium accelerates the removal of water vapour molecules from an evaporating surface such as a hydrogel or water-rich medium.
By adjusting electrode spacing and voltage, users can tune both wind speed and cooling intensity, achieving portable, scalable, and ultra-efficient sub-ambient cooling.
Laboratory results demonstrated:
Cooling power enhancements of up to 88% at low voltages (~5 kV).
- Cooling
- Coefficient of Performance (COP) > 1000, far surpassing conventional evaporative coolers (COP 10–80).
- Hydrogel media outperform liquid water in maintaining colder surface temperatures due to reduced convection losses, offering safe, spill-free cooling adaptable to irregular or vertical surfaces.
Applications & Advantages
This cooling enhancer is ideal for passive sub-ambient cooling applications where energy availability is constrained but reliable cold storage is essential.
- Cold-chain logistics: Ensuring stable sub-ambient storage for vaccines, biologics, and fresh produce during transport, particularly in off-grid or resource-limited regions.
- Rural and humanitarian aid: Portable coolers for food and medicine distribution in underdeveloped regions without consistent refrigeration.
- Consumer and commercial cooling: Integration into food delivery platforms or last-mile distribution boxes to reduce reliance on ice or bulky powered refrigeration.
- Building and infrastructure cooling: Scalable hydrogel coatings or panels for passive temperature regulation on walls, rooftops, and solar farms.
- Specialised electronics and data centres: Supplementing convective cooling with ionic wind-driven evaporative mechanisms for localised, energy-efficient heat management.


.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=9b7345be_1)

.tmb-listing.jpg?Culture=en&sfvrsn=b5366f51_1)








